Network Fundamental -IPv6 - CCNA - P3
Configure and verify IPv6 addressing and prefix

IPv6
IPv6 is the newest version of the IP protocol. IPv6 was developed to overcome many deficiencies of IPv4, most notably the problem of IPv4 address exhaustion. IPv4, which has only about 4.3 billion (2 to the power of 32) available addresses, IPv6 allows for 3.4 × 10 to the power of 38 addresses.

IPv6 features
Here is a list of the most important features of IPv6:
- Large address space: IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, which means that for each person on the Earth there are 48,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 addresses!
- Enhanced security: IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) is built into IPv6 as part of the protocol . This means that two devices can dynamically create a secure tunnel without user intervention.
- Header improvements: the packed header used in IPv6 is simpler than the one used in IPv4. The IPv6 header is not protected by a checksum so routers do not need to calculate a checksum for every packet.
- No need for NAT: since every device has a globally unique IPv6 address, there is no need for NAT.
- Stateless address autoconfiguration: IPv6 devices can automatically configure themselves with an IPv6 address.
Address format of IPv6
IPv4, which uses a dotted-decimal format with each byte ranges from 0 to 255, IPv6 uses eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons. For example, this is a valid IPv6 address:
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7332
Here is a couple of more examples that can help you grasp the concept of IPv6 address shortening
Long version: 1454:0045:0000:0000:4140:0141:0055:ABBB
Shortened version: 1454:45::4140:141:55:ABBB
Long version: 0000:0000:0001:AAAA:BABC:A222:BABA:0001
Shortened version: ::1:AAAA:BABC:A222:BABA:1
Types of IPv6 addresses
- Unicast – represents a single interface. Packets addressed to a unicast address are delivered to a single interface.
- Anycast – identifies one or more interfaces. For example, servers that support the same function can use the same unicast IP address. Packets sent to that IP address are forwarded to the nearest server. Anycast addresses are used for load-balancing. Known as “one-to-nearest” address.
- Multicast – represent a dynamic group of hosts. Packets sent to this address are delivered to many interfaces. Multicast addresses in IPv6 have a similar purpose as their counterparts in IPv4.
IPv6 unicast
Unicast addresses represent a single interface. Packets addressed to a unicast address will be delivered to a specific network interface.
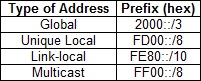
- global unicast – similar to IPv4 public IP addresses. These addresses are assigned by the IANA and used on public networks. They have a prefix of 2000::/3, (all the addresses that begin with binary 001).
- unique local – similar to IPv4 private addresses. They are used in private networks and aren’t routable on the Internet. These addresses have a prefix of FD00::/8.
- link local – these addresses are used for sending packets over the local subnet. Routers do not forward packets with this addresses to other subnets. IPv6 requires a link-local address to be assigned to every network interface on which the IPv6 protocol is enabled. These addresses have a prefix of FE80::/10.
IPv6 address prefixes
Verify IP parameters for Client OS (Windows, Mac OS, Linux)
It's nothing but a checking the IP Address of the NIC in the system.Like check the ip address and subnet mask and Gateway of route in the system.We can use some specific commands to get details of the above mentioned parameters
Windows-ipconfig
linux-ifconfig
Mac OS-ipconfig getifaddr en0
Wireless principles
Wi-Fi is a high speed internet connection and network connection without use of any cables or wires. The wireless network is operating three essential elements that are radio signals, antenna and router. The radio waves are keys which make the Wi-Fi networking possible.

| Type | Range | Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Personal area network (PAN) | Within reach of a person | Bluetooth, ZigBee, NFC |
| Local area network (LAN) | Within a building or campus | IEEE 802.11 (WiFi) |
| Metropolitan area network (MAN) | Within a city | IEEE 802.15 (WiMAX) |
| Wide area network (WAN) | Worldwide | Cellular (UMTS, LTE, etc.) |
Explain virtualization fundamentals (virtual machines)
Virtualization is the process of creating a software-based, or virtual, representation of something, such as virtual applications, servers, storage and networks. It is the single most effective way to reduce IT expenses while boosting efficiency and agility for all size businesses.
Examples:VMware,Virtual Box,Parallels,QEMU,Windows Virtual PC.
Switching concepts
It is process to forward packets coming in from one port to a port leading towards the destination. When data comes on a port it is called ingress, and when data leaves a port or goes out it is called egress. A communication system may include number of switches and nodes.
Mainly using the common two types of switching
1.Packet switching
2.Circuit Switching




Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You for your Response....